Adsorbency vs. Absorbency: What Is the Difference?
Feb 17, 2022

In surface chemistry, the adsorption and absorption phenomenon describe what happens in the interface between two surfaces, including solids, gases, and liquids. Absorption and adsorption are often confused due to their similarity in name but describe a different physical and chemical interaction between materials.
There are many industrial and environmental applications to absorption and adsorption processes, including water purification and refrigeration. Our sorption guide can help you understand the key differences between each sorption process with examples of its industrial use in action.
What Is Sorption?
Sorption refers to the physical and chemical processes where a substance attaches to another. In the sorption process, the sorbent is the material that collects molecules of another substance. The sorbate is the substance that gets attached to the sorbent. Adsorption and absorption are two types of sorption processes.
Absorption vs. Adsorption: What Is the Difference?

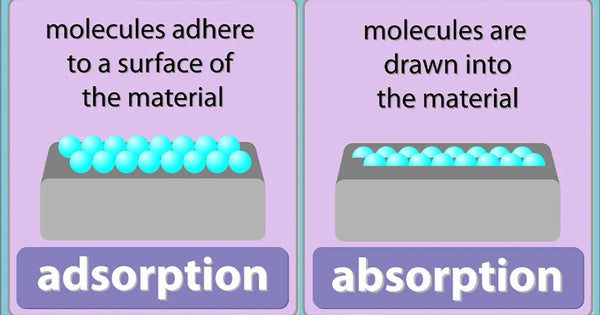
Absorption refers to a process where a liquid, gas, or solid material completely soaks up a liquid or gas through a chemical or physical process. Adsorption refers to a physical or chemical process where a solid substance holds molecules of a gas, liquid, or solute on its outside or internal surface.
What Is Absorption? Uniform Dissolution

The absorption process is a bulk phenomenon in which molecules are taken in by the bulky material. During the process, the molecules are completely diffused or dissolved into the material, forming a solution. When dissolved, the molecules are hard to split up from the absorbent material.
Physical and Chemical Absorption
Physical absorption is a non-reactive process affected by properties of the liquid or gas, such as solubility, pressure, and temperature. Chemical absorption occurs when chemicals in one substance are absorbed by chemicals in another, such as when gases are absorbed by a solid or liquid.
Examples of Absorption
Skin Absorption

In dermal absorption, a substance from the environment penetrates several layers in the surface of the skin or crosses the blood-brain barrier. Skin absorption allows either medicine or toxic chemicals to passively or actively enter the body.
In medical uses, application of a topical medicine over the affected area is used for localized relief. The passive absorption process can also allow harmful substances to enter the skin. Long-term dermal exposure to harmful chemicals may result in system toxicity.
Since the skin absorption process is passive, there is no need to expend energy for the process to occur. The dermal absorption process is affected by the condition of the skin, amount of substance applied, location on the body, duration of application, and solubility of the substance.
Digestive Absorption
Absorption occurs during the digestion process in the body. When we ingest a food or drink, the digestive system selectively absorbs nutrients and water from the substance. Unlike dermal absorption, digestive absorption requires energy to select the substances for absorption.
As the food or drink passes through the small and large intestine, the epithelium surface on these organs absorbs the nutrients and water that can then enter into the bloodstream. Most chemical absorption occurs in the small intestine.
Absorption Refrigeration
Absorption refrigeration systems start by evaporating refrigerant liquid, which is absorbed by a separate liquid to maintain a low partial pressure. The refrigerant liquid is then heated to remove the heat from the refrigerator.
What Is Adsorption? A Surface Phenomenon
The adsorption process occurs during the adhesion of molecules to the surface of a liquid or solid. Since the process is a surface phenomenon, the molecules only adhere to the inner or outer surface of the substance, without penetrating the material.
In the adsorption process, the adsorbate is the substance whose molecules get attached to the adsorbent’s surface. The adsorbent is the insoluble material where the adsorption process occurs. The process can be classified into physical and chemical adsorption.
Adsorption has numerous industrial applications, including activated charcoal, water purification, moisture and humidity removal, adsorption chromatography, air conditioning, and much more. In the pharmaceutical industry, adsorption is used to lengthen neurological exposure to certain drugs or components of them.
Physical vs. Chemical Adsorption
Physical adsorption, or physisorption, usually refers to the build-up of adsorbed materials on a solid substance due to weak forces called Van der Waals forces. Chemical adsorption, or chemisorption, occurs when the adsorbed materials are adhered by a chemical bond.
Examples of Adsorption

The spread of living systems like viruses occurs through the process of adsorption. At first, the virus attaches itself and is adsorbed on the surface of the cells to begin the viral replication process. The adsorption process occurs when certain proteins on the viral capsid bind to the cell receptors.
Adsorption Chromatography with Activated Carbon and Other Adsorbents
Adsorption chromatography is an analytical separation technique used to capture minor particles in a mixture. During the process, a liquid or gas mobile phase is passed through the solid-state stationary phase.
As the mixture filters through the stationary phase, different particles will adhere to the stationary phase at different rates. This process can be used to separate particles with higher and lower affinity to the stationary phase.
Compounds with low affinity rush through the stationary phase while compounds with a high affinity for the substance are trapped within the surface area of the stationary phase.
Adsorption chromatography can use manufactured (activated carbon) or natural (zeolite) adsorbents. Activated alumina, silica gel, and activated carbon, also known as activated charcoal, are effective at absorbing contaminants from various substances. For example, activated alumina is used in water filtration to remove fluoride, arsenic, sulfur, and lead.
Key Differences Between Adsorption and Adsorption
Definition
Adsorption occurs when the liquid, gas, or solid sticks on the surface of the adsorbent. Absorption happens when the solid, liquid, or gas soak up into the surface of the absorbent.
Phenomenon
Absorption refers to a bulk phenomenon where the absorbate penetrates the absorbent. Adsorption is a surface phenomenon where certain particles in the adsorbate adhere to the surface of the adsorbent.
Filter Media Sample Request
Interested in trying our filter media? We would love to send you some! Browse our products, then fill out this form and someone from our team will be in touch to finalize your request.
Heat Exchange
Absorption is an endothermic process where external energy is required, increasing the energy of the absorbent material. Adsorption is an exothermic process where the surface energy decreases, leading to reduced residual forces of the surface.
Rate
Absorption occurs at a uniform rate. Adsorption occurs at an increased initial rate and gradually decreases when equilibrium is reached.
Temperature
The absorption process does not depend on temperature. The adsorption process is affected by temperature.
Concentration
The concentration of the absorbing material is the same throughout the absorbent. During adsorption, the adsorbent has a higher concentration of the adsorbate on its surface than on any other part.
Color Remediation in the Cannabis Industry

In the cannabis industry, the adsorption process has been used to purify and separate cannabinoids and terpenes from different types and qualities of biomass. Media Bros provides BHO, CO2, and ethanol cannabis extractors with innovative color remediation filter media and hardware to improve the color and clarity of extracts.